Did you know the U.S. enrichment capacity is so small that it has to import uranium fuels from Russia until this day?
Even though the U.S. was the first nation to harness nuclear power for both military and electricity generation, it has become heavily dependent on other countries in the field of nuclear energy. Despite nuclear supplies for about 20% of electricity generation in the U.S., the nation has imported nearly all the nuclear fuel required to produce this energy.
Simply put, the U.S. lacks a nuclear supply chain. But before we go any further, we should understand how uranium is converted into nuclear fuel.
From Ore to Fuel
The mined uranium must be processed into nuclear fuel to run a nuclear reactor and generate electricity. The uranium miner cleaned the sand to get triuranium octoxide (U3O8). This U3O8 form are the common form for transportation, storage, and… investment. (We’ll talk about investment part in the future Chronicles). The U3O8 consists of 99.3% of U-238, 0.7% U-235, and very small U-234. The heavy part of uranium processing is to increase the concentration of U-235 to way above 0.7%.
Through the conversion process, the U3O8 is then converted into a gas called uranium hexafluoride (UF6). This gas is then fed into the enrichment process.
During the enrichment process, the UF6 gas molecules containing U-235 are separated from U-238 and others. The gas was then collected and condensed back into liquid form. To be a weapon, there must be a very high (>90%) concentration of U-235.
Through the fabrication process, the liquid UF6 is processed into fuel rods. These will be used in nuclear reactors in power plants.
There are two broad types of nuclear fuel. The low concentrate (<5% of U-235) is called LEU (low-enriched uranium). The most recent technology is called HALEU (high-assay LEU). HALEU has a higher concentration of <20% U-235. Because it has a higher concentration, the nuclear reactor can be smaller in size, and the fuel rod is less frequent to replace. This is called a small modular reactor (SMR).
The SMR are very attractive in terms of cost, safety and practicality. Even Indonesia, who are blessed with cheap coal, are planning to build nuclear power plant with SMR technology helped by U.S. companies.
Who’s Powered Our Nuclear Power Plants
The United States has lost the majority of its uranium processing capability. The culprits are numerous, ranging from safety concerns to nuclear waste fears to low petroleum prices.
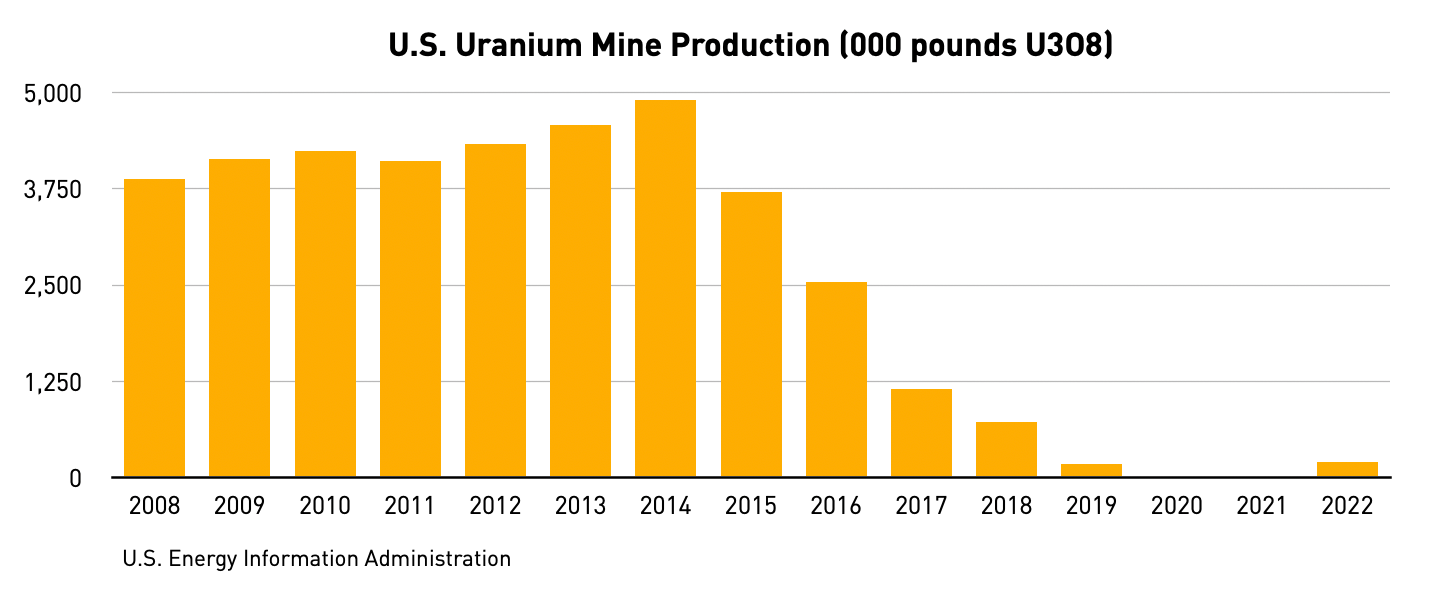
The majority of uranium mines have closed in the last decade. By the end of 2022, the U.S. will have only 5 uranium mines, down from 20 in 2009. The remaining mines are similarly quite small. Their overall output is only 194,000 pounds of U3O8, compared to more than 4 million pounds in 2009.
There are no uranium enrichment plant in the U.S. except those owned by Urenco (a European company) and Centrus Energy (a U.S. company). Centrus has just started this year, becoming the first U.S. owned company that produced HALEU. Meanwhile, Urenco’s enrichment is only enough to cover 27% of national demand.
Bear in mind that currently, there is no SMR (and HALEU) demand in the U.S. SMR is a new technology, and only Russia and China have active SMR power plants. Other countries, including the U.S., are still in the planning, design, or development phases.
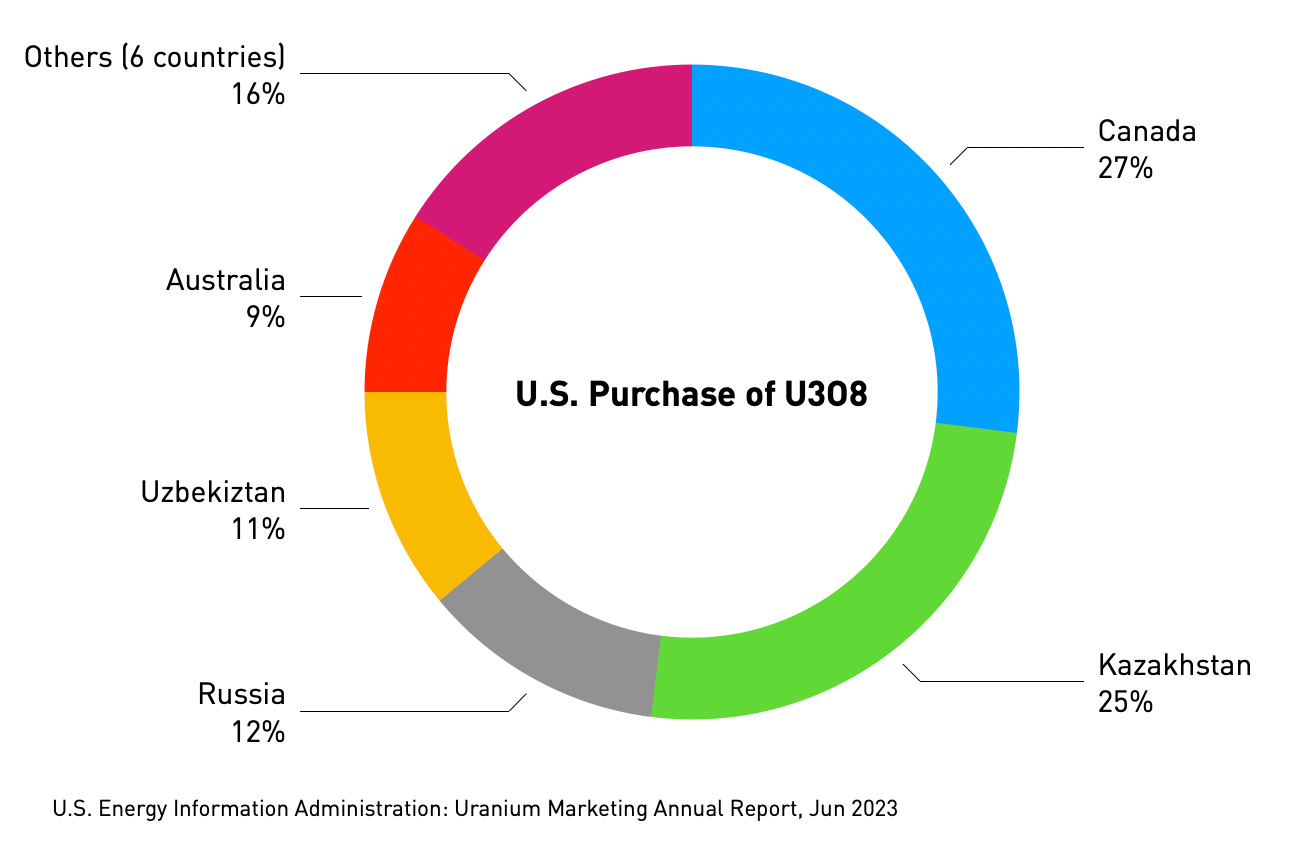
So, where does our nuclear fuel come from? The U.S. imports 32.1 million pounds of U3O8, accounting for 99% of domestic demand.
The U.S. also imports 73% of its enriched uranium requirements from a variety of countries, including Russia and China. Russia accounts for around 33% of overall imports of enriched uranium.
The U.S. is On the Race Again
One of the warning signs was the Russia-Ukraine war. The United States sanctioned Russia in all areas, including the use of SWIFT facilities and US Treasury securities. However, there is one that remains unsanctioned: Russian nuclear fuel shipments.
Coincidentally, nuclear initiatives have received political attention in the last two years. Three bills have been introduced to increase nuclear capacity. The Nuclear Fuel Security Act, introduced in early 2023, was the most current. The bill will cover a variety of programs aimed at improving nuclear fuel security in the U.S. For example, the Department of Energy (DOE) will be required to acquire 20 tons of HALEU per year until 2027, as well as 100 tons of LEU per year. In comparison, Centrus Energy only produces 600kg of HALEU each year. The bill also requires DOE to improve programs to expand nuclear workforce capacity.
It will be interesting to see if this government intervention succeeds in getting the US back into the nuclear race.
One thing for sure, just now, Urenco’s US branch is on hiring spree.
IPO — We’ve Got A Joke, So Listen Up!
The IPO from the previous week included a biotechnology firm, a financial institution, a technology-driven real estate company (known as "proptech"), and a producer in the oil and natural gas industry.
Now, do you know why did the biotech company go to the bank to talk about real estate and oil? Because they wanted to genetically engineer a tree that grows money and oil on their properties!"
Okay, that’s not funny, but at least we’ve tried…
ABVX 0.00%↑ Abivax S.A. is a biotech company working on treatments that use the body's natural mechanisms to control the immune response in people with chronic inflammatory diseases. The company is testing its main drug, Obefazimod, in phase 3 trials for treating adults with moderate to severe ulcerative colitis, a chronic inflammatory bowel disease.
CPBI 0.00%↑ Central Plains Bancshares, Inc. was incorporated on June 13, 2023, and has not engaged in any business to date. Upon completion of the conversion and stock offering, Central Plains Bancshares, Inc. will register as a savings and loan holding company, which operates under the name “Home Federal Bank,” a federally-chartered mutual savings association headquartered in Grand Island, Nebraska. Historically, Home Federal Bank was founded by Buck Beltzer in May of 1935 in Grand Island.
AIRE 0.00%↑ reAlpha Tech Corp. is a real estate technology company utilizing and commercializing its AI-focused technology stack to empower retail investor participation in short-term rental properties, specifically by providing equity crowdfunding investments in private placements.
MNR 0.00%↑ Mach Natural Resources LP, an independent upstream oil and gas company focused on the acquisition, development and production of oil, natural gas and NGL (natural gas liquid) reserves in the Anadarko Basin region of Western Oklahoma, Southern Kansas and the panhandle of Texas.